Tutorial
-
The 7Cs Framework Explained: Building Effective Digital Experiences
A website or digital platform is more than just design and content. It must communicate clearly, guide users, build trust, and deliver value. Many digital experiences fail not because of poor traffic, but because the experience itself is confusing or misaligned with user needs. The 7Cs Framework provides a structured way to evaluate and improve…
Written by

-
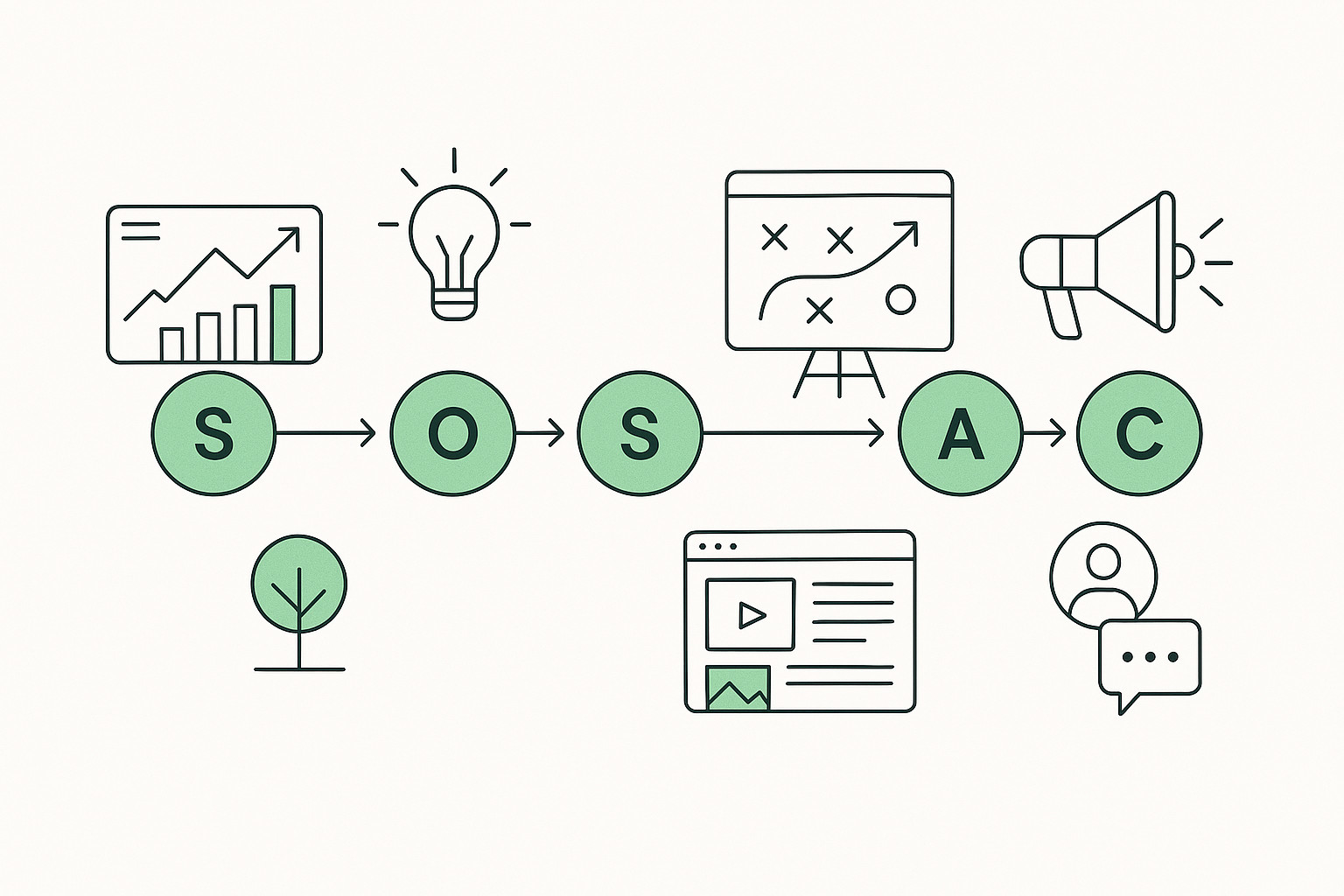
SOSTAC® Framework Explained: A Practical Guide to Digital Marketing Planning
Many digital marketing plans fail not because teams lack tools or creativity, but because they lack a clear planning structure. Activities are executed without alignment, objectives are unclear, and results become difficult to measure. The SOSTAC® framework solves this by providing a logical, step-by-step model for planning, executing, and controlling digital marketing strategies. In this…
Written by
-
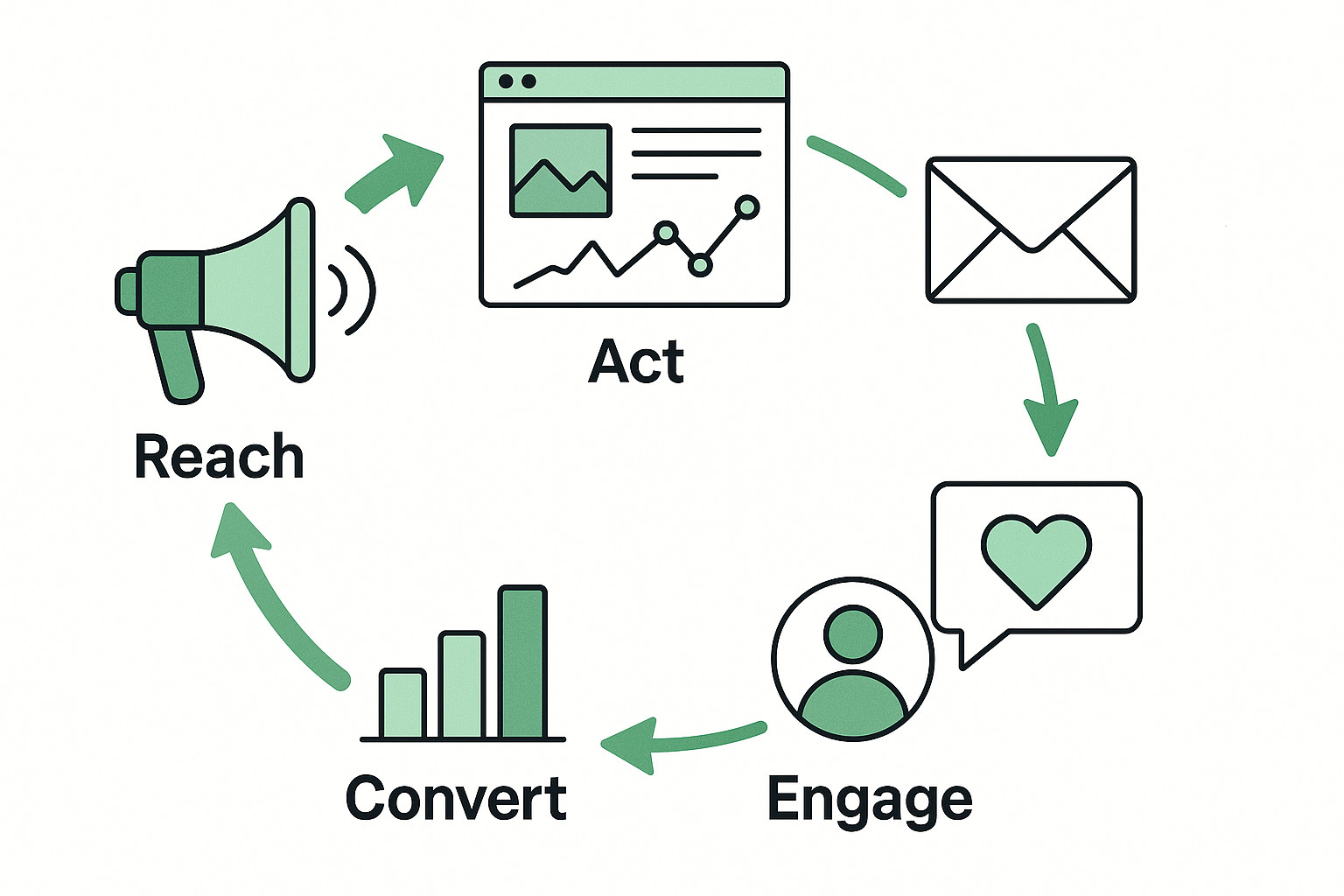
The RACE Framework Explained: A Practical Guide to Planning Digital Marketing
Digital marketing often fails not because of poor tools or lack of budget, but because of poor structure. Teams run ads, post on social media, send emails, and publish content without a clear system to connect everything together. The RACE Framework solves this problem by providing a simple, customer-centric structure for planning, executing, and measuring…
Written by
-
Digital Marketing Foundations: Customer Journey Basics (Awareness → Conversion)
Imagine you’re at a bustling farmer’s market. You stroll past vibrant stalls, each showcasing unique products. Suddenly, a tantalizing aroma catches your attention. You approach the source-a stall selling freshly baked bread. The baker greets you with a warm smile and offers you a sample. Intrigued, you try it and find it delightful. Before you…
Written by
-
Email Marketing Basics: Why Email Still Matters
In the fast-paced world of digital marketing, where social media and influencer campaigns dominate the conversation, it’s easy to overlook the humble email. Yet, email marketing remains a cornerstone of effective communication strategies for businesses of all sizes. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore why email still matters, how to leverage it effectively, and the…
Written by

-
Digital Marketing Foundations: Email Marketing 101
Imagine this: You’re scrolling through your inbox, and amidst the clutter of promotional emails, one stands out. It’s personalized, engaging, and offers something you can’t resist. Welcome to the world of email marketing, a powerful tool in the digital marketer’s arsenal. Whether you’re a budding entrepreneur, a seasoned professional, or someone looking to enhance their…
Written by

-
Email Marketing Basics: Writing Effective Newsletters
Imagine this: You’ve just launched a new product, and you’re excited to share it with your audience. You’ve crafted the perfect email, but when you hit ‘send,’ it feels like you’re shouting into the void. Sound familiar? Crafting an effective newsletter is both an art and a science. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the…
Written by

-
Digital Marketing Foundations: Basics of PPC Advertising
Imagine you’re at a bustling marketplace, and every vendor is shouting to attract your attention. In the digital world, Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising is like those vendors, but instead of shouting, they’re using algorithms and targeted ads to catch your eye. Whether you’re a student, a professional, an entrepreneur, or even a retiree looking to understand…
Written by

